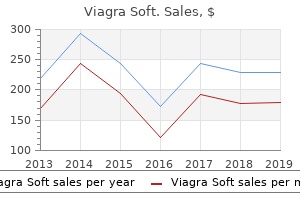


"Buy viagra soft 50 mg fast delivery, erectile dysfunction treatment after radical prostatectomy".
By: Q. Zuben, M.A., M.D.
Deputy Director, Loma Linda University School of Medicine
While these changes are occurring in chromosomes erectile dysfunction treatment implant video cheap viagra soft, a number of other events are also taking place diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction epidemiology pathophysiology and management best order for viagra soft. They produce a number of microtubules that pass from one centriole to the other and form a spindle causes of erectile dysfunction young males purchase 50mg viagra soft free shipping. Metaphase: With the formation of the spindle erectile dysfunction pills from india 50mg viagra soft free shipping, chromosomes move to a position midway between the two centrioles. Anaphase: the centromere of each chromosome splits longitudinally into two so that the chromatids now become independent chromosomes. One chromosome of each such pair now moves along the spindle to either pole of the cell. Telophase: In this phase, the two daughter nuclei are formed by appearance of nuclear membranes. In this process, the organelles are presumably duplicated and each daughter cell comes to have a full complement of them. Cell multiplication is equally necessary after the birth of the individual for growth and for replacement of dead cells. We have seen that chromosomes within the nuclei of cells carry genetic information that controls the development and functioning of various cells and tissues; and, therefore, of the body as a whole. When a cell divides, it is essential that the entire genetic information within it be passed on to both the daughter cells resulting from the division. In other words, the daughter cells must have chromosomes identical in number (and in genetic content) to those in the mother cell. A different kind of cell division called meiosis occurs during the formation of the gametes. This consists of two successive divisions called the first and second meiotic divisions. The daughter cells in turn have their own span of activity, followed by another division. The period during which the cell is actively dividing is the phase of mebooksfree. Zygotene: the 46 chromosomes in each cell consist of 23 pairs (the X- and Y-chromosomes of a male being taken as a pair). The two chromosomes of each pair come to lie parallel to each other, and are closely apposed. There are two central and two peripheral chromatids, one from each chromosome. The two central chromatids (one belonging to each chromosome of the bivalent) become coiled over each other so that they cross at a number of points. For sake of simplicity only one such crossing is shown in Figure First Meiotic Division Prophase: the prophase of the first meiotic division is prolonged and is usually divided into a number of stages as follows: Leptotene: the chromosomes become visible (as in mitosis). Although each chromosome consists of two chromatids, these cannot be distinguished at this stage. At the site where the chromatids cross, they become adherent; the points of adherence are called chiasmata. As they do so, the chromatids involved in crossing over "break" at the points of crossing and the "loose" pieces become attached to the opposite chromatid. Metaphase: As in mitosis the 46 chromosomes become attached to the spindle at the equator, the two chromosomes of a pair being close to each other. Anaphase: the anaphase differs from that in mitosis in that there is no splitting of the centromeres. The resulting daughter cells, therefore, have 23 chromosomes, each made up of two chromatids. Telophase: the anaphase is followed by the telophase in which two daughter nuclei are formed. Second Meiotic Division the first meiotic division is followed by a short interphase. Such duplication is unnecessary as chromosomes of cells resulting from the first division already possess two chromatids each. However, because of the crossing over that has occurred during the first division, the daughter cells are not identical in genetic content. Clinical correlation Nondisjunction After splitting of centromere one or more chromosomes fail to migrate properly due to abnormal function of achromatic spindle.
The amniotic sac and chorionic cavity have been opened to expose the embryo b12 injections erectile dysfunction purchase viagra soft 100mg free shipping, showing the bushy appearance of the trophoblast at the embryonic pole in contrast to small villi at the abembryonic pole impotence psychological discount viagra soft amex. The difference between the embryonic and abembryonic poles of the chorion is also reflected in the structure of the decidua erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus pdf cheap viagra soft 100mg, the functional layer of the endometrium erectile dysfunction water pump buy viagra soft online now, which is shed during parturition. The decidua over the chorion frondosum, the decidua basalis, consists of a compact layer of large cells, decidual cells, By the beginning of the fourth month, the placenta has two components: (1) a fetal portion, formed by the chorion frondosum and (2) a maternal portion, formed by the decidua basalis. This zone, characterized by decidual and syncytial giant cells, is rich in amorphous extracellular material. By this time, most cytotrophoblast cells have Fused decidua parietalis, chorion laeve and amnion Decidua basalis Decidua parietalis Chorionic cavity Chorion frondosum Placenta Amniotic cavity Yolk sac Decidua capsularis Chorion laeve Uterine cavity Amniotic cavity A B Figure 8. The amnion and chorion have fused, and the uterine cavity is obliterated by fusion of the chorion laeve and the decidua parietalis. Between the chorionic and decidual plates are the intervillous spaces, which are filled with maternal blood. They are derived from lacunae in the syncytiotrophoblast and are lined with syncytium of fetal origin. During the fourth and fifth months,the decidua forms a number of decidual septa, which project into intervillous spaces but do not reach the chorionic plate. These septa have a core of maternal tissue, but their surface is covered by a layer of syncytial cells, so that at all times, a syncytial layer separates maternal blood in intervillous lakes from fetal tissue of the villi. As a result of this septum formation, the placenta is divided into a number of compartments, or cotyledons. Because the decidual septa do not reach the chorionic plate, contact between intervillous spaces in the various cotyledons is maintained. As a result of the continuous growth of the fetus and expansion of the uterus, the placenta also enlarges. Its increase in surface area Chorionic vessel Cervix of uterus Umbilical cord Figure 8. Portions of the wall of the uterus and the amnion have been removed to show the fetus. The umbilical cord is tightly wound around the abdomen, possibly causing abnormal fetal position in the uterus (breech position). Chapter 8 Third Month to Birth: the Fetus and Placenta 105 Endometrial veins Decidual plate Spiral artery Decidual septum Amnion Chorionic plate Umbilical vessels Chorionic vessels Figure 8. Most of the intervillous blood returns to the maternal circulation by way of the endometrial veins. The increase in thickness of the placenta results from arborization of existing villi and is not caused by further penetration into maternal tissues. Attachment of the umbilical cord is usually eccentric and occasionally even marginal. Rarely, however, does it insert into the chorionic membranes outside the placenta (velamentous insertion). Circulation of the Placenta Full-Term Placenta At full term, the placenta is discoid with a diameter of 15 to 25 cm, is approximately 3 cm thick, and weighs about 500 to 600 g. At birth, it is torn from the uterine wall and, approximately 30 minutes after birth of the child, is expelled from the uterine cavity as the afterbirth. When the placenta is viewed from the maternal side, 15 to 20 slightly bulging areas, the cotyledons, covered by a thin layer of decidua basalis, are clearly recognizable. A number of large arteries and veins, the chorionic Cotyledons receive their blood through 80 to 100 spiral arteries that pierce the decidual plate and enter the intervillous spaces at more or less regular intervals. Pressure in these arteries forces the blood deep into the intervillous spaces and bathes the numerous small villi of the villous tree in oxygenated blood. As the pressure decreases, blood flows back from the chorionic plate toward the decidua, where it enters the endometrial veins. Hence, blood from the intervillous lakes drains back into the maternal circulation through the endometrial veins. Collectively, the intervillous spaces of a mature placenta contain approximately 150 mL Figure 8.
All brand names and product names used in this book are trade names erectile dysfunction treatment nyc order discount viagra soft on-line, service marks erectile dysfunction caused by spinal stenosis viagra soft 100 mg free shipping, trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners erectile dysfunction treatment nz quality 100mg viagra soft. The publisher is not associated with any product or vendor mentioned in this book erectile dysfunction drugs and nitroglycerin discount viagra soft 50mg free shipping. This book is designed to provide accurate, authoritative information about the subject matter in question. However, readers are advised to check the most current information available on procedures included and check information from the manufacturer of each product to be administered, to verify the recommended dose, formula, method and duration of administration, adverse effects and contraindications. It is the responsibility of the practitioner to take all appropriate safety precautions. Neither the publisher nor the author(s)/editor(s) assume any liability for any injury and/or damage to persons or property arising from or related to use of material in this book. This book is sold on the understanding that the publisher is not engaged in providing professional medical services. If such advice or services are required, the services of a competent medical professional should be sought. Every effort has been made where necessary to contact holders of copyright to obtain permission to reproduce copyright material. If any have been inadvertently overlooked, the publisher will be pleased to make the necessary arrangements at the first opportunity. Notwithstanding 35 years of experience in teaching embryology and several publications in human developmental anatomy, I was skeptical because it is simply difficult for anyone to match the simplicity of expression and sheer elegance of images so diligently originated by Prof. With the encouragement provided by the publishers and colleagues, I have taken the proverbial plunge. When I started my career as a medical teacher way back in 1981, I used to reproduce the diagrams from Prof. Like all its previous editions, this is also a one person effort which clearly offers scope for improvement. Suggestions from academics, students and professionals are welcome for incorporation in the coming editions. K Thyagaraju, Assistant Professor, for drawing and Photoshop editing several of the figures. Some of the figures in the present edition originated from the research carried out by the postgraduate students in my lab. I am also thankful to Shri Jitendar P Vij (Group Chairman), Mr Ankit Vij (Group President) of M/s Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd, New Delhi, India, for kindly agreeing to publish this book, and the production team especially Ms. The subject of embryology has traditionally been studied from imported textbooks of anatomy or of embryology. Experience has shown that the treatment of the subject in most of these books is way above the head of the average medical student in India. The difficulty has increased from year to year as there has been, and continues to be, progressive deterioration in the standards of the teaching of English in our schools and colleges. The combination of unfamiliar sophistications of language and of an involved technical subject, has very often left the student bewildered. In this book, care has been taken to ensure that the text provides all the information necessary for an intelligent understanding of the essential features of the development of various organs and tissues of the human body. At the same time, several innovations have been used to make the subject easy to understand. Secondly, simultaneous references to the development of more than one structure have been avoided as far as possible. While this has necessitated some repetition, it is hoped that this has removed one of the greatest factors leading to confusion in the study of this subject. Thirdly, almost every step in development has been shown in a simple, easy to understand, illustration. As far as possible, the drawings have been oriented as in adult anatomy to facilitate comprehension. Fourthly, the chapters have been arranged so that all structures referred to at a particular stage have already been adequately introduced.
Elevation ofthe heat resistance of vegetative cells and spores of Clostrldium perfringens type A by sublethal heat shock impotence pills for men buy cheap viagra soft 100mg line. The effects of pressure on certain micro organisms encountered in the preservation of fruits and vegetables erectile dysfunction treatment philadelphia buy 100mg viagra soft. Hydrostatic pressure is like high temperature and oxidative stress in the damage it causes to yeast what is an erectile dysfunction pump buy discount viagra soft 100mg on line. Ther mal inactivating behavior ofBacillus stearotherrnophilus under high pressure impotence quad hoc buy generic viagra soft on line. Hydrostatic pressure and eiec troporation have increase bactericidal efficiency in combination with bacteriocins. Interaction of hydrostatic pressure, time and temperature of pressurization and pediocin AcH on inactivation of foodborne bacteria. Changes in tea components during processing and preservation of tea extract by hydrostatic pressure sterilization. Factors affecting the resistance of Listeria monocytogenes to high hydrostatic pressure. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on heat- resistant and heat-sensitive strains of Salmonella. Inhibition ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae by combination of hydrostatic pressure and monoterpenes. Shelf-life extension, safety and quality of fresh pork loin treated with high hydrostatic pressure. Variation in resis tance ofnatural isolates ofEscherichia coli 0157 to high hydrostatic pressure, mild heat, and other stresses. High pressure inactivation of Byssochlamys nivea ascospores and other heat-resistant moulds. Effects of high pressure and bacteriostatic agents on the destruction of citrobacter freundii in minced beef muscle. Microbial and chemical shelf life of high-pressure treated salmon cream at refrigeration temperatures. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on the temperature dependence ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii. Initiation of germination and inactivation of Bacillus pumilus spores by hydrostatic pressure. Use of high hydrostatic pressure and irradiation to eliminate Ciostridium sporogenes in chicken breast. High pressure and freezing pretreatment effects on drying, rehydration, texture and color of green beans, carrots and potatoes. High-pressure inactivation and sublethal injury ofpressure-resistant Escherichia coll mutants in fruit juices. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas Ouorescens strains in bovine milk. Inactivation of bacterial spores In phosphate buffer and in vegetable cream treated at high pressures. Reduction of Bacillus steatothermophilus spores by combined high pressure and temperature treatments. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on chatacteristics of pork slurries and inactivation of microorganisms associated with meat and meat products. The effect of high hydrostatic pressure on Listeria monocytogenes in phosphate-buffered saline and model food systems. The effect of high hydrostatic pressure on the activity of intracellulat enzymes of Listeria monocytogenes. Effect of pressure and temperature on the death rates of lactobaclllus casei and escherlchla coli. Effect of concurrent high hydrostatic pressure, acidity and heat on the injury and destruction of Listeria monocy togenes. Response of Listeria monocytogenes and Vibrio parahaemolytlcus to high hydrostatic pressure.
Cheap viagra soft 50mg otc. Signs of Depression डिप्रेशन के सर्वसाधारण संकेत(इशारे)Dr Kelkar Mental Illness mind ed.